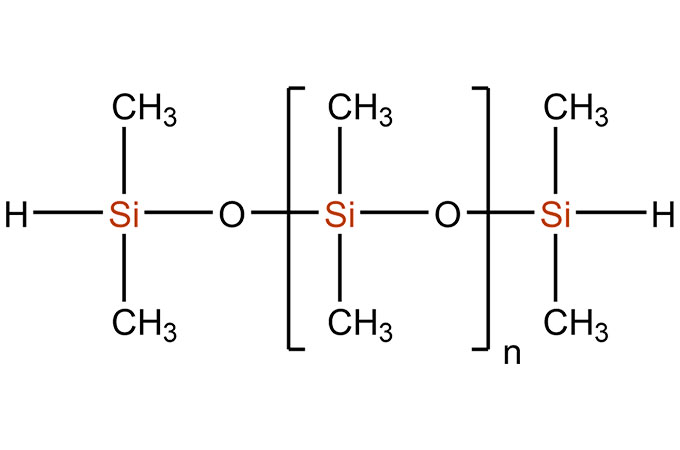
Organic silane, or organosilicon compounds, refers to compounds containing Si-C bonds and at least one organic group directly connected to the silicon atom. It is customary to also regard those compounds that connect organic groups with silicon atoms through oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen, etc., as organosilicon compounds. Among them, the polysiloxane composed of silicon-oxygen bond (-Si-O-Si-) is the largest, most researched and most widely used type among organosilicon compounds, accounting for more than 90% of the total amount.
1. The characteristics of organic silane
Temperature resistance characteristics:
Organic silane products are based on the silicon-oxygen (Si-O) bond as the main chain structure, the bond energy of the C-C bond is 82.6 kcal/mole, the bond energy of the Si-O bond is 121 kcal in the organosilane. Therefore, organosilane products have high thermal stability, and the chemical bonds of molecules will not break or decompose under high temperature (or radiation exposure). Organosilane is not only resistant to high temperature, but also resistant to low temperature, and can be used in a wide temperature range. Whether it is chemical properties or physical mechanical properties, the change with temperature is very small.
Weather resistance:
The main chain of organic silane products is -Si-O-, there is no double bond, so it is not easy to be decomposed by ultraviolet light and ozone. Organic silane has better thermal stability, radiation resistance and weather resistance than other polymer materials. The service life of organic silanes in the natural environment can reach several decades.
Electrical insulation performance:
As a reliable silane manufacturer, we made organic silane products that have good electrical insulation properties. Their dielectric loss, withstand voltage, arc resistance, corona resistance, volume resistivity and surface resistivity are among the best insulating materials. Moreover, their electrical performance is very little affected by temperature and frequency. Therefore, they are a kind of stable electrical insulating materials, which are widely used in the electronics and electrical industries. In addition to excellent heat resistance, organic silanes also have excellent water repellency, which guarantees high reliability of electrical equipment used in wet conditions.
Biological characteristics:
Biologically active organic silane is an essential nutrient for the human body. Organosilane is an important element that constitutes human tissues and participates in metabolism. It is stored in every cell of the human body and serves as a support for cell construction, while helping to absorb other important substances such as magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium. The human body can only continuously obtain organic silanes through food.
Low surface tension and low surface energy:
The main chain of organo silanes is very flexible, and its intermolecular force is much weaker than that of hydrocarbons. Therefore, it has lower viscosity than hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight, weak surface tension, low surface energy, and strong film-forming ability. This low surface tension and low surface energy are the main reasons for its various applications: hydrophobicity, silicone defoamer, foam stability, anti-sticking, lubrication, glazing and other excellent properties.
2. Use of organosilane
Because organic silane has the above-mentioned excellent properties, its application range is very wide. It is not only used as a special material for aviation, cutting-edge technology, and military technology departments, but also used in various sectors of the national economy. Its application range has been expanded to: construction, electronic and electrical, textile, automobile, machinery, leather and papermaking, chemical and light industry, metal and paint, medicine and medical treatment, etc.
 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية tiếng việt
tiếng việt